Metabolic Syndrome
Medical review by Albert J. Hart, MD
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a medical term for a constellation of health symptoms or markers related to insulin resistance in the body.
It is also called Syndrome X, a term coined by Gerald Reaven, the researcher who first identified and described the MetS condition. Having MetS indicates an increase in the risk of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease and other health disturbances.
Insulin resistance is a condition in which chronically high levels of blood sugar and insulin have caused the body’s mechanism for regulating insulin and blood glucose (sugar) to fail. If left untreated, being insulin resistant usually leads to MetS, prediabetes and possibly a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
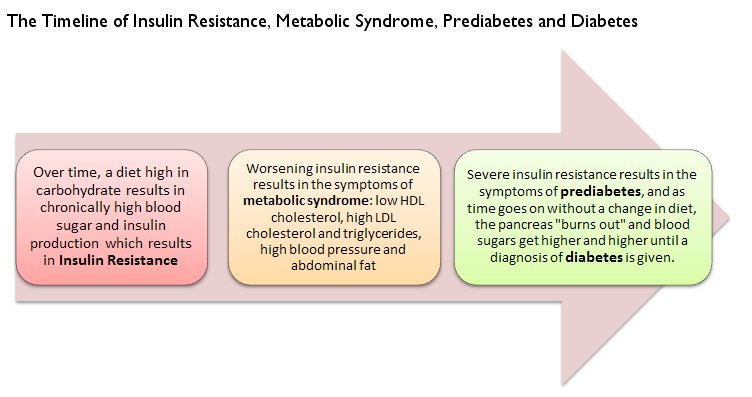
In fact, I believe that people who are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes had insulin resistance which progressed over time to MetS and prediabetes before they were given a final diagnosis of T2D. If someone has MetS, it's a warning sign that more serious metabolic conditions can develop in the future in a linear fashion:
- Insulin sensitivity becomes damaged: A high carb diet and a lack of exercise causes the cells of the liver and muscles to become resistant to insulin's message to store sugar.
- Metabolic Syndrome develops. Baseline blood sugars begin to rise, high blood pressure, deranged blood cholesterol and abdominal obesity develop.
- Pre diabetes is not far behind. The resistance to insulin worsens over more time until pre diabetic symptoms develop and blood sugar and insulin are chronically high.
- Pre diabetes finally worsens into type 2 diabetes: If left untreated, the pre diabetes worsens, more and more insulin is needed to control blood sugar, the pancreatic ability to function becomes damaged, and eventually full blown type 2 diabetes develops.
Diagnosing Metabolic Syndrome
The diagnosis of MetS is done by looking at a specific set of health parameters. A person can be diagnosed with MetS or "Syndrome X" if three out of the five following health characteristics is present in his medical examination:
- HDL cholesterol levels below 40 mg/dl for men, and 50 mg/dl women
- Blood triglycerides above 150 mg/dl
- Blood pressure above 130/85, or use of a blood pressure medication
- Excessive abdominal fat: a waist circumference greater than 40 inches in men, and 30 inches in women.
- Fasting blood sugars above 100 mg/dl
Some people may have all of these symptoms, others may exhibit just three, but all of these health symptoms are individually associated with the development of prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
In a research paper by Jeff Volek and Richard Feinman, MetS is defined as a condition of "intolerance to carbohydrate." They also state that "Although there is no universally accepted definition or mechanism, a rough common denominator is the set of five features: obesity (high body weight, BMI and/or waist circumference), high glucose and insulin levels, low HDL, high TAG and high blood pressure. Involvement of insulin resistance is generally a common feature and a likely causative agent for at least some of the symptoms.A subset of these metabolic markers, the TAG:HDL ratio, has been proposed as a simple marker for identifying insulin resistance."
The TAG:HDL ratio refers to comparing the levels of blood triglycerides to HDL cholesterol measurements.
Treating Metabolic Syndrome
Not surprisingly, the most effective treatment for MetS is a ketogenic diet. The goal is to reduce the insulin resistance which is at the root of MetS, and a ketogenic diet is specifically designed to do this. In this study, the researchers discussed the large body of evidence showing that a low carbohydrate diet reverses all of the diagnostic factors associated with MetS.
Other trials have shown that ketogenic diets are more effective than low fat diets AND more effective than low glycemic diets. And this meta analysis review confirmed that low carb diets are effective in treating MetS.
More Information
All of my books are available in electronic PDF, and now in paperback on Amazon!
 |
 |
 |
|
Buy paperbook on Buy paperback on Amazon Buy the e-Book via Paypal |
Buy paperback on Buy paperback on Amazon Buy the e-Book via Paypal |
Buy paperback on Buy paperback on Amazon Buy the e-Book via PayPal |